Token Ring gets defined as the local area network which has the properties to transmit the node only when it has certain pieces in succession that come from the other successive nodes turn by turn. Ethernet gets defined as the system used for connecting various computers to form a local area network and has different protocols to ensure the passage of information takes place smoothly.
Comparison Chart
| Basis of Distinction | Token Ring | Ethernet |
| Definition | The local area network which has the properties to transmit the node only when it has certain pieces in succession that come from the other successive nodes turn by turn. | The system used for connecting various computers to form a local area network and has different protocols to ensure the passage of information takes place smoothly. |
| Working | Deterministic | Non-deterministic |
| Delays | Delay start to occur whenever the load becomes low. | The flow stays the same even if the load becomes less or more. |
| Type | A token-passing system which has only one workstation to call upon at one instant. | Collision Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) topology. |
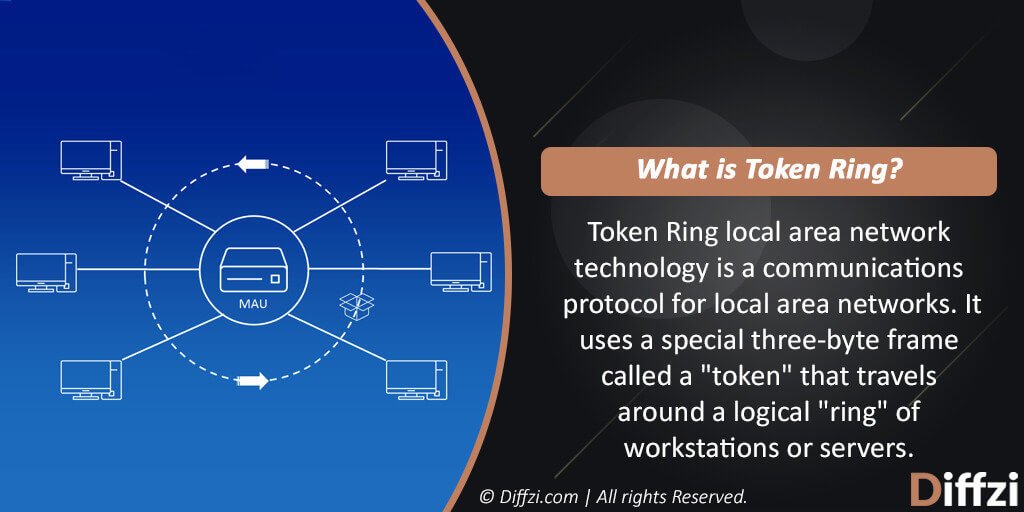
What is Token Ring?
Token Ring gets defined as the local area network which has the properties to transmit the node only when it has certain pieces in succession that come from the other successive nodes turn by turn. A token ring system is a neighborhood (LAN) in which all PCs are associated in a ring or star topology and pass at least one coherent tokens from the host to have. Just a host that holds a token can send information, and tokens are discharged when receipt of the information gets affirmed. Token ring systems keep data bundles from crashing on a network portion since information must get sent by a token holder and some tokens accessible get controlled.
A token, which is an extraordinary piece design, goes around the circle. To communicate something specific, a PC gets the token, appends a message to it, and afterward gives it a chance to keep on traveling around the system. Additionally, observe token passing. Presented by IBM in 1984, it was then institutionalized with convention IEEE 802.5 and was genuinely compelling, especially in professional workplaces, yet progressively obscured by the following forms of Ethernet.
Stations on a token ring LAN are intelligently sorted out in a ring topology with information being transmitted successively starting with one ring station then onto the next with a control token coursing around the ring controlling access. Comparative token-passing systems get utilized by ARCNET, token transport, 100VG-AnyLAN (802.12) and FDDI, and they have hypothetical favorable circumstances over the CSMA/CD of raw Ethernet.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet gets defined as the system used for connecting various computers to form a local area network and has different protocols to ensure the passage of information takes place smoothly, and no simultaneous transmission occurred. At the point when first sent in the 1980s, Ethernet upheld the greatest possible data rate of 10 megabits for each second (Mbps).
Afterward, supposed “Quick Ethernet” norms expanded this most significant information rate to 100 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet innovation additionally stretches out pinnacle execution up to 1000 Mbps, and 10 Gigabit Ethernet innovation likewise exists.
Ethernet is the most generally introduced neighborhood (LAN) change. Ethernet is a connection layer convention in the TCP/IP stack, depicting how organized gadgets can arrange information for transmission to other system devices on a similar system fragment, and how to put that information out on the network association. It touches both Layer 1 (the physical layer) and Layer 2 (the data interface layer) on the OSI arrange convention show.
The total length of individual Ethernet links gets restricted to around 100 meters; however Ethernet systems can be effectively reached out to connection whole schools or office structures utilizing system connect gadgets. Ethernet characterizes two units of transmission, parcel, and casing. The edge incorporates the “payload” of information getting transmitted as well as tending to data distinguishing the physical “Media Access Control” (MAC) locations of both sender and beneficiary, VLAN labeling and nature of administration data, and blunder adjustment data to identify issues in transmission.
Key Differences
- Token Ring gets defined as the local area network which has the properties to transmit the node only when it has certain pieces in succession that come from the other successive nodes turn by turn.
- Ethernet gets defined as the system used for connecting various computers to form a local area network and has different protocols to ensure the passage of information takes place smoothly.
- The nature of Ethernet always stays non-deterministic, on the other hand, the kind of token ring always remains deterministic.
- Whenever the load stays lower the number of delays starts to increase when it comes to the token ring, on the other hand, whenever the pressure becomes depressed, the Ethernet does not have any delays.
- The token ring becomes known as a token-passing system which has only one workstation to call upon at one instant. On the other hand, the Ethernet becomes known as Collision Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) topology, and that means different workstations stay active at one instant.
- The speed of both these systems differ from each other and becomes 100M bit/s for Ethernet that stays several times faster than the 16M bit/s token ring.
- The price of Ethernet stays much less than the price of a token ring and becomes $15 and $25 respectively.