The difference between Male and Female Urethra is in the span. In males, the urethra is 8 inches long, and in females, urethra is only two inches long. Male urethra has distinguished into four parts whereas female urethra has no differentiation.
Word “urethra” is derived from the Greek language. It’s a tube in placental mammals that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the elimination of fluids especially urine from the body to the outside world. The male urethra is larger in length than the female urethra. Another difference could be the path the urine takes getting in the bladder to the outside world. In males, the path is much more curving and in females that the path is much more direct. This curved route makes the catheterization of males harder. Due to the brief length of the urethra in females, the disease can be a problem.
Comparison Chart
| Basis | Male Urethra | Female Urethra |
| LENGTH | Its length is about 20 cm | It’s nearly 4 cm in length |
| DIAMETER | 8-9 mm | 6 mm |
| PARTS | It has four components; pre-prostatic area; prostatic area, membranous and penial. | It’s no specific regions. |
| OPENING | It opens at the peak of the penis by the urinogenital aperture. | It opens in the front of the vaginal aperture from the urinary aperture. |
| ROLE | It transports urine in addition to semen into the exterior. | It transports only urine into the exterior. |
| Frequent DISEASES | Kidney stones | Urethritis and kidney stones |
What is Male Urethra?
Males use their urethra for 2 functions, ejaculation and urination. The external sphincter of the male urethra is striated muscle which allows voluntary control over urination and this extra internal urethral sphincter muscle is present only in males. Semen travels through the urethra during sex in males.
The urethra joins the bladder, the collection site for urine to the outside world. In males, the urethra is eight inches long and divides into four parts. The first part is pre-prostatic urethra that’s an intramural portion of the organ and approximately 0.5 to 1.5 cm in length based upon the fullness of the bladder. Its second part is prostatic urethra which spans through the prostate gland.
There are numerous openings; the ejaculatory duct gets sperms in the vas deferens and ejaculates fluid from the seminal vesicle; many prostatic ducts where fluid in the prostate passes and leads to the semen; the prostatic utricle, which is merely an indentation. These openings are known as verumontanum collectively. The third portion of the male urethra is membranous urethra that’s a small part passing through the external urethral sphincter and nearly 1 to 2 cm in length. This is the smallest in diameter component of the urethra. It’s within the deep perineal pouch.
The bulbourethral glands and located anterior to the area but available in the spongy urethra. Its fourth part is spongy urethra that runs across the length of the penis on its ventral surface. It’s nearly 15 to 16 cm in length and travels throughout the corpus spongiosis. The duct from the urethral gland enters here. The opening parts of the bulbourethral glands are also found here. The path of pee getting from the bladder to the outside world is much more curving which produces a characterization of males harder than females.

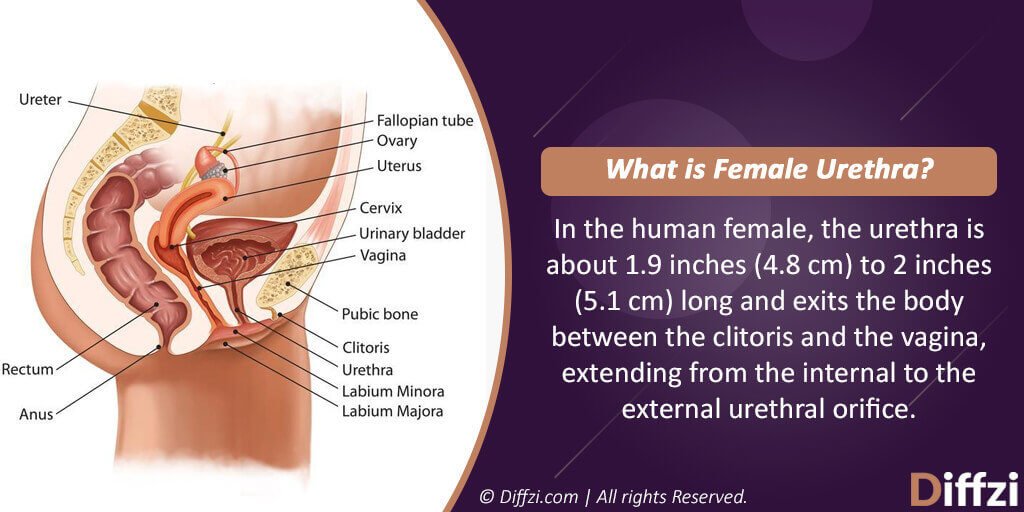
What is Female Urethra?
The female urethra is the section of the female urinary system. It’s developed in the endoderm and the splanchnic mesoderm of the urogenital sinus. The paramesonephric tubercle divides the urogenital sinus into pelvic which will become a vesicourethral unit and a phallic part that later becomes a vagina.
Female urethra develops in the 12th gestational week. The female urethra is relatively a simple tubular structure which has the sole purpose of urination. It’s a brief organ without a complicated investing structure. It’s a richly vascular spongy cylinder and is intended to offer continence. Although female urethra less likely to intrinsic pathology in comparison with male urethra but the disease can be started due to its short length.
Urethritis is a common inflammation of the urethra. Additionally, it causes painful urination. Urethritis may also be caused by bacterial and viral infections. Its symptoms are urgent pus and bleeding such as excretions and sparks. Treatment of urethritis depends upon the specific causes and symptoms but mostly involve various kinds of medicines. Kidney stones is another disorder that strikes female urethra.
Key Differences between Male Urethra and Female Urethra
- The male urethra is more than female urethra in length
- Both are important elements of human anatomy useful for excretion.
- In females, the path in which urine takes getting in the bladder to the outside world is much more direct.
- In males, the path in which urine takes getting in the bladder to the outside world is much more curving.