Food is a fundamental source of energy for all living organisms in the ecosystem. A series or chain of organisms where each of them is determined by one and other as a source of energy or food is called a food chain. The food chain is further be divided into two major types; Grazing Food Chain and Detritus Food Chain.
The main difference between these kinds of food chain is that grazing food chain begins from the green plants, which are the principal producers, whereas detritus food chain starts from the dead organic matter or decomposed material, that is usually within the soil. The energy to the grazing food chain comes in sunlight as the autotrophs (green plants) prepare their food (photosynthesis) amid the existence of the sunlight. while the energy for the detritus food chain is taken in the detritus or the decomposed materials.
Comparison Chart
| Basis | Grazing Food Chain | Detritus Food Chain |
| Definition | The grazing food chain begins in the autotrophs (green plants). | Detritus food chain starts from the detritivores. |
| Energy Supply | In grazing food chain the energy is taken from the sunlight as green plants prepare food in the presence of it. | In detritus food chain the main energy source is stay of detritus. |
| Organisms | In grazing food chain macroscopic organisms are included. | In detritus food chain subsoil organisms are involved, that could be macroscopic or microscopic. |
| Number of Energy | Produces a less quantity of energy into the air. | Produces a great quantity of energy to the air. |
What is Grazing Food Chain?
The grazing food chain is one of the significant varieties of the food chain that’s viewed as a food chain procedure dominantly happening in organisms. The grazing food chain begins from the autotrophs (green plants), the significant energy for this series is taken in sunlight as the plants carry out the process of photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight. The green plants operate as the principal producer of the sort of food chain; after the herbivores become fed upon the green plants.
The chain goes on farther as the primary consumers (herbivores) are consumed by the secondary consumers (omnivores) in this kind of food chain. This food chain does not consist of germs or other decomposers; it’s carried out from the microscopic organisms. The grazing food chain is an easier kind of food chain as it starts from the main producers (green plants), who are the dominant producers in various ecosystems throughout the planet. The name of the food chain itself informs it has the green plants as a significant source or the one starting off the series.

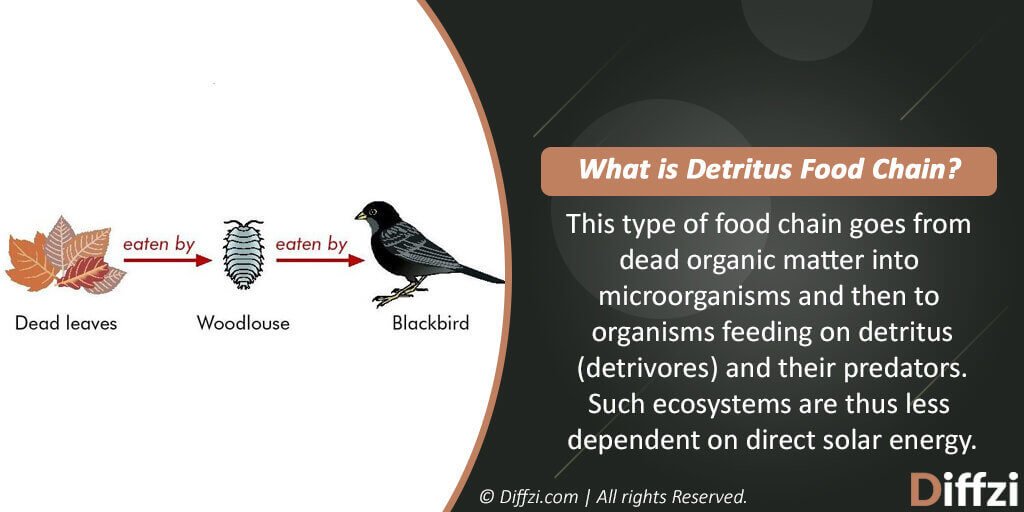
What is Detritus Food Chain?
The detritus food chain is the sort of food chain which ensures maximum usage and minimal wastage of the available material. This food chain begins from the dead organic matter or other similar wastes; farther, this material is consumed by the creature, and later this creature gets eaten by another animal from the soil. The series keeps on going until the organic matter consists. This sort of food chain is very useful in the fixation of inorganic nutrients and using it to the maximum.
Detritus food chain has the remains of detritus as a significant source of energy, and this procedure gets completed by the subsoil organisms, which could be macroscopic or microscopic. Unlike the grazing food chain, the detritus food chain generates a massive quantity of energy to the air.
Key Differences between Grazing Food Chain and Detritus Food Chain
- The grazing food chain begins from the autotrophs (green plants), whereas the detritus food chain starts from the detritivores.
- In grazing food chain the energy is taken from the sunlight as green plants prepare food in the presence of it while at the detritus food chain the primary energy source is stay of detritus.
- In grazing food chain macroscopic organisms are involved, on the other hand, in the detritus food chain, subsoil organisms are involved, which could be macroscopic or microscopic.
- Contrary to the grazing food chain, the detritus food chain generates a massive quantity of energy to the air.